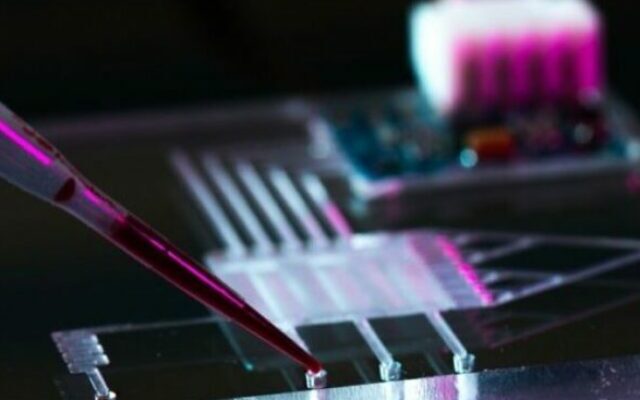
ABSTRACT:
Microfluidics studies are basically the study of fluids in micrometer and nanometer scales.By manipulating the fluids this interdisciplinary field helps in many distinct fields of science like chemistry, biology, physical sciences and has practical applications on molecular analysis, microelectronics, molecular biology etc. One of the applications of microfluidics is LOC(lab on chip) devices which bring revolution in modern science. Lab on chip(LOC) devices integrate functions of the lab in a few centimeter circuit with the help of microfluidic channels and active and passive components. Capillary forces are used to control passive flow and microvalves, micropumps are the components of active microfluidics. Other than LOC(lab on chip) microfluidics are used to build devices like DNA chips, micropropulsion , micro thermal technologies, 2 photon polymerization etc.
TYPES OF MICROFLUIDIC FLOWS:
Generally the microfluidic flow should be with in 10 x 10
μm of space but over the years many techniques have been developed. Some of them are —
1) OPEN MICROFLUIDICS: In open microfluidics one of the boundaries is removed which causes the exposure of the fluid to the air or another second fluid. Paper based microfluidics, thread based microfluidics are examples of open microfluidics.
2) CONTINUOUS FLOW MICROFLUIDICS: In continuous flow microfluidics fluids are manipulated in a continuous manner through microchannels. External mechanisms like micropumps, microvalves and internal mechanisms like capillary forces are used in this system.
3) DROPLET BASED MICROFLUIDICS: In a microfluidic chip engraved with microfluidic channels, droplet size can be controlled with the help of other fluids. Each droplet acts as a microreactor. It is used in cosmetic creams, diagnostic tests, and controlled medicine delivery.
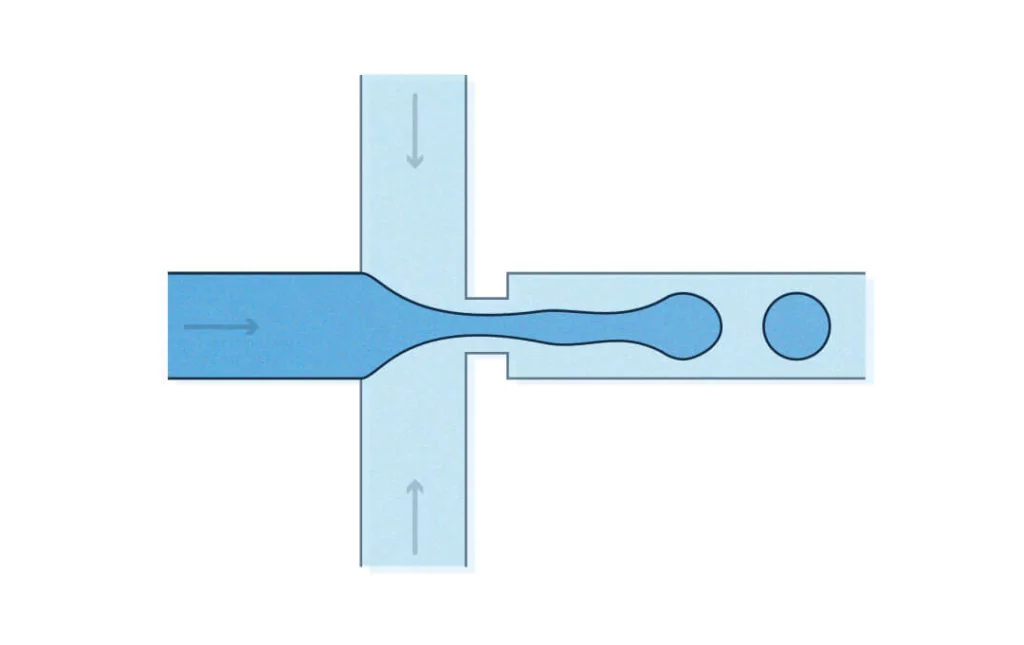
4) DIGITAL MICROFLUIDICS: In digital microfluidics discrete units of droplets are being manipulated with the help of electrowetting. Droplets are mixed, moved, reacted, separated, analyzed with various
procedures like optical electrowetting, mechanical actuation, electrochemical processes, mass spectroscopy etc.
5) PAPER BASED MICROFLUIDICS: In paper based microfluidics paper or other porous membranes are used which rely on the capillary action. Paper based microfluidics are cheap, portable, easy to dispose of, that’s why it is user friendly. Some applications of paper based microfluidics are point of care(POC) diagnostic devices, glucose detection, environment testing etc.

6) PARTICLE DETECTION MICROFLUIDICS: It is done by the principle of Coulter current. An electrical signal is generated when a weak conducting fluid passes through a very small sized pore and the current is proportional to the ratio of particle volume and pore volume.
Current ∝ particle volume / pore volume
The size of RBC and WBC are measured with this process.
APPLICATIONS:
Microfluidics are one of the most versatile fields which has applications over every field of science. From inkjet printhead to lab on chip(LOC), from point of care(POC) diagnosis to bio smoke alarm, it has applications everywhere.
C. ELEGANS IMMOBILIZATION: C. elegans is a very simple nematode which has a nervous system. But in order to get the high resolution images we need to immobilize the nematode. Microfluidics can resolve this issue by trapping the nematode and by manipulating them in a microfluidic device.
POINT OF CARE: One of the best applications of microfluidics, it is also called bedside testing. Because of the cheapness, disposability, rapidness, minimal sample consumption, it is used for pregnancy testing,
HIV diagnosis, glucose biosensors etc.
CELL ANALYSIS: Many researchers are pushing in this field because it has a great possibility in future. We need to increase the sensibility because the system size decreases to the size of a cell. In microfluidic devices we can precisely monitor the cell cell, cell medium, cell substrate interaction.
PH CONTROL: LOC is one of the main microfluidic applications. It can be used to observe the response of the sample to different kinds of drugs. pH is one of the most important parameters and to measure it we used techniques like electrolyte insulator semiconductor(EIS) and ion selective field effect
transistor(ISFET).
GRADIENT GENERATION: Gradients play a really important role in many biological processes. But creating a gradient is a really crucial step. Because of the very small size of microfluidic flow, only diffusion is possible. That’s why diffusive mixing is used to develop gradients.

DNA CHIPS(MICROARRAYS): In DNA chips DNA fragments are fixed on the pieces of glass and plastic. Similar to DNA chips, protein chips are also used to determine the presence of protein.

MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: Electrophoresis, PCR amplification, liquid chromatography are the applications of microfluidics which are based on the principles of cell separation, cell analysis and cell manipulation.
EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY: If we combine microfluidics with landscape ecology we can make synthetic landscapes for bacterial habitat. If we study bacterial adaptations in those synthetic landscapes, then we can answer many questions of evolutionary biology.
ACOUSTIC DROPLET EJECTION(ADE): This technology injects small volumes of liquids without any physical contact. ADE technology can easily transfer proteins, DNA, living cells without any damage to the system.
FUTURE OF MICROFLUIDICS:
What will be the future of microfluidics? Well if we look at its applications
this question is not that hard to answer. It can also be used for circulating tumor cell(CTC) and non circulating tumor cell(non CTC) biopsy. Because of the cost effective and user friendly nature of microfluidics it is used in medical diagnosis in many developing countries. There are many fields where development is required. This is just the beginning, microfluidics will have
rapid growth in the near future.
REFERENCES:
1. Microfluidics – Wikipedia( https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microfluidics )
What is your reaction?
Excited
1
Happy
1
In Love
1
Not Sure
0
Silly
0


